WhatWeb is an advanced website fingerprinter that can identify content management systems (CMS), blogging platforms, statistic/analytics packages, JavaScript libraries, web servers, embedded devices, version numbers, email addresses, account IDs, web framework modules, SQL errors, and more.
It has over 1700 plugins, each to recognize something different. It can be stealthy and fast, or thorough but slow.
WhatWeb supports an aggression level to control the tradeoff between speed and reliability.
WhatWeb supports an aggression level to control the tradeoff between speed and reliability.
When you visit a website in your browser, the transaction includes many hints of what web technologies are powering that website. Sometimes a single web page visit contains enough information to identify a website but when it does not, WhatWeb can interrogate the website further.
The default level of aggression, called 'stealthy', is the fastest and requires only one HTTP request of a website. This is suitable for scanning public websites.
Most WhatWeb plugins are thorough and recognize a range of cues from subtle to obvious. For example, most WordPress websites can be identified by the meta HTML tag, e.g. '', but a minority of WordPress websites remove this identifying tag but this does not thwart WhatWeb. The WordPress WhatWeb plugin has over 15 tests, which include checking the favicon, default installation files, login pages, and checking for "/wp-content/" within relative links.
Features:
- Over 1700 plugins.
- Control the trade-off between speed/stealth and reliability.
- Plugins include example URLs.
- Performance tuning. Control how many websites to scan concurrently.
- Multiple log formats: Brief (greppable), Verbose (human readable), XML, JSON, MagicTree, RubyObject, MongoDB.
- Proxy support including TOR.
- Custom HTTP headers.
- Basic HTTP authentication.
- Control over web page redirection.
- Nmap-style IP ranges.
- Fuzzy matching.
- Result certainty awareness.
- Custom plugins defined on the command line.
Usage
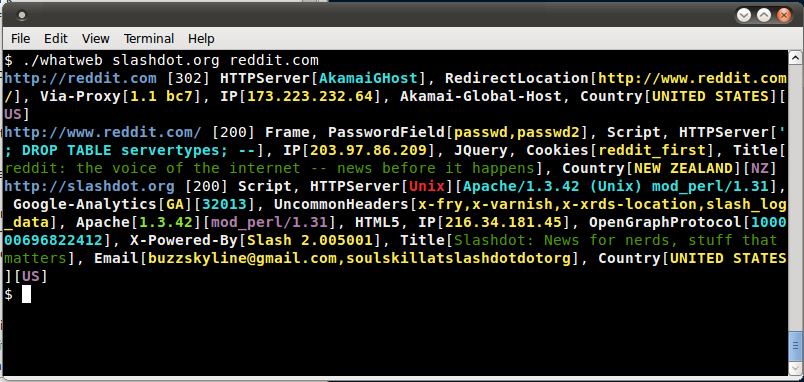
Usage: whatweb [options] <URLs> TARGET SELECTION: <TARGETs> Enter URLs, hostnames, IP adddresses, filenames, or nmap-format IP address ranges. --input-file=FILE, -i Read targets from a file. You can pipe hostnames or URLs directly with -i /dev/stdin. TARGET MODIFICATION: --url-prefix Add a prefix to target URLs. --url-suffix Add a suffix to target URLs. --url-pattern Insert the targets into a URL. Requires --input-file, eg. www.example.com/%insert%/robots.txt AGGRESSION: The aggression level controls the trade-off between speed/stealth and reliability. --aggression, -a=LEVEL Set the aggression level. Default: 1. Aggression levels are: 1. Stealthy Makes one HTTP request per target. Also follows redirects. 2. Unused 3. Aggressive If a level 1 plugin is matched, additional requests will be made. 4. Heavy Makes a lot of HTTP requests per target. Aggressive tests from all plugins are used for all URLs. HTTP OPTIONS: --user-agent, -U=AGENT Identify as AGENT instead of WhatWeb/0.4.8-dev. --header, -H Add an HTTP header. eg "Foo:Bar". Specifying a default header will replace it. Specifying an empty value, eg. "User-Agent:" will remove the header. --follow-redirect=WHEN Control when to follow redirects. WHEN may be `never', `http-only', `meta-only', `same-site', `same-domain' or `always'. Default: always. --max-redirects=NUM Maximum number of contiguous redirects. Default: 10. AUTHENTICATION: --user, -u=<user:password> HTTP basic authentication. --cookie, -c=COOKIES Provide cookies, e.g. 'name=value; name2=value2'. PROXY: --proxy <hostname[:port]> Set proxy hostname and port. Default: 8080. --proxy-user <username:password> Set proxy user and password. PLUGINS: --list-plugins, -l List all plugins. --info-plugins, -I=[SEARCH] List all plugins with detailed information. Optionally search with keywords in a comma delimited list. --search-plugins=STRING Search plugins for a keyword. --plugins, -p=LIST Select plugins. LIST is a comma delimited set of selected plugins. Default is all. Each element can be a directory, file or plugin name and can optionally have a modifier, eg. + or - Examples: +/tmp/moo.rb,+/tmp/foo.rb title,md5,+./plugins-disabled/ ./plugins-disabled,-md5 -p + is a shortcut for -p +plugins-disabled. --grep, -g=STRING Search for STRING in HTTP responses. Reports with a plugin named Grep. --custom-plugin=DEFINITION Define a custom plugin named Custom-Plugin, Examples: ":text=>'powered by abc'" ":version=>/powered[ ]?by ab[0-9]/" ":ghdb=>'intitle:abc \"powered by abc\"'" ":md5=>'8666257030b94d3bdb46e05945f60b42'" --dorks=PLUGIN List Google dorks for the selected plugin. OUTPUT: --verbose, -v Verbose output includes plugin descriptions. Use twice for debugging. --colour,--color=WHEN control whether colour is used. WHEN may be `never', `always', or `auto'. --quiet, -q Do not display brief logging to STDOUT. --no-errors Suppress error messages. LOGGING: --log-brief=FILE Log brief, one-line output. --log-verbose=FILE Log verbose output. --log-errors=FILE Log errors. --log-xml=FILE Log XML format. --log-json=FILE Log JSON format. --log-sql=FILE Log SQL INSERT statements. --log-sql-create=FILE Create SQL database tables. --log-json-verbose=FILE Log JSON Verbose format. --log-magictree=FILE Log MagicTree XML format. --log-object=FILE Log Ruby object inspection format. --log-mongo-database Name of the MongoDB database. --log-mongo-collection Name of the MongoDB collection. Default: whatweb. --log-mongo-host MongoDB hostname or IP address. Default: 0.0.0.0. --log-mongo-username MongoDB username. Default: nil. --log-mongo-password MongoDB password. Default: nil. PERFORMANCE & STABILITY: --max-threads, -t Number of simultaneous threads. Default: 25. --open-timeout Time in seconds. Default: 15. --read-timeout Time in seconds. Default: 30. --wait=SECONDS Wait SECONDS between connections. This is useful when using a single thread. HELP & MISCELLANEOUS: --short-help Short usage help. --help, -h Complete usage help. --debug Raise errors in plugins. --version Display version information. (WhatWeb 0.4.8-dev). EXAMPLE USAGE: * Scan example.com. ./whatweb example.com * Scan reddit.com slashdot.org with verbose plugin descriptions. ./whatweb -v reddit.com slashdot.org * An aggressive scan of wired.com detects the exact version of WordPress. ./whatweb -a 3 www.wired.com * Scan the local network quickly and suppress errors. whatweb --no-errors 192.168.0.0/24 * Scan the local network for https websites. whatweb --no-errors --url-prefix https:// 192.168.0.0/24 * Scan for crossdomain policies in the Alexa Top 1000. ./whatweb -i plugin-development/alexa-top-100.txt \ --url-suffix /crossdomain.xml -p crossdomain_xml
Logging & Output
The following types of logging are supported:- --log-brief=FILE (Brief, one-line, greppable format)
- --log-verbose=FILE (Verbose)
- --log-xml=FILE (XML format, XSL stylesheet is provided)
- --log-json=FILE (JSON format)
- --log-json-verbose=FILE (JSON verbose format)
- --log-magictree=FILE (MagicTree XML format)
- --log-object=FILE (Ruby object inspection format)
- --log-mongo-database (Name of the MongoDB database)
- --log-mongo-collection (Name of the MongoDB collection. Default: whatweb)
- --log-mongo-host (MongoDB hostname or IP address. Default: 0.0.0.0)
- --log-mongo-username (MongoDB username. Default: nil)
- --log-mongo-password (MongoDB password. Default: nil)
- --log-errors=FILE (Log errors. This is usually printed to the screen in red.)
You can output to multiple logs simultaneously by specifying multiple command line logging options.
Plugins
Note: All plugins are loaded by default.Matches are made with:
- Text strings (case-sensitive)
- Regular expressions
- Google Hack Database queries (limited set of keywords)
- MD5 hashes
- URL recognition
- HTML tag patterns
- Custom ruby code for passive and aggressive operations
To list the plugins supported:
$ ./whatweb -l
To view more detail about a plugin or search plugins for a keyword:
Examples:
$ ./whatweb -I <plugin>
Plugins can be selected by directories, files or plugin names as a comma delimited list with the -p or --plugin command line option.
Each list item may have a modifier: + adds to the full set, - removes from the full set and no modifier overrides the defaults.
Examples:
- --plugins +plugins-disabled,-foobar
- --plugins +/tmp/moo.rb
- --plugins foobar (only select foobar)
- -p title,md5,+./plugins-disabled/
- -p ./plugins-disabled,-md5
The --dorks <plugin name> command line option returns google dorks for the selected plugin.
For example, --dorks WordPress returns "is proudly powered by WordPress"
The --grep, -g command line option searches the target page for the selected string and returns a match in a plugin called Grep if it is found.
Aggression
WhatWeb features several levels of aggression. By default, the aggression level is set to 1 (stealthy) which sends a single HTTP GET request and also follows redirects.
- Stealthy (level 1) - Makes one HTTP request per target. Also, follows redirects.
- Unused (level 2)
- Aggressive (level 3) - Can make a handful of HTTP requests per target. This triggers aggressive plugins for targets only when those plugins are identified with a level 1 request first.
- Heavy (level 4) - Makes a lot of HTTP requests per target. Aggressive tests from all plugins are used for all URLs.
Level 3 aggressive plugins will guess more URLs and perform actions that are potentially unsuitable without permission.
Performance & Stability
WhatWeb features several options to increase performance and stability.
- --max-threads, -t (Number of simultaneous threads. Default: 25)
- --open-timeout (Time in seconds. Default: 15)
- --read-timeout (Time in seconds. Default: 30)
- --wait=SECONDS (Wait SECONDS between connections. This is useful when using a single thread.)
The --wait and --max-threads commands can be used to assist in IDS evasion.
Changing the user-agent using the -U or --user-agent command line option will avoid the Snort IDS rule for WhatWeb.
If you are scanning ranges of IP addresses, it is much more efficient to use a port scanner like nmap to discover which have port 80 open before scanning with WhatWeb.
Character set detection, with the Charset plugin dramatically decreases performance by requiring more CPU. This is required by JSON and MongoDB logging.
Optional Dependencies
- To enable JSON logging, install the json gem.
- To enable MongoDB logging, install the mongo gem.
- To enable character set detection and MongoDB logging, install the rchardet gem.
WhatWeb - An Advanced Website Fingerprinter Hacking Tool
 Reviewed by AC10 Tech
on
Friday, March 02, 2018
Rating:
Reviewed by AC10 Tech
on
Friday, March 02, 2018
Rating:
 Reviewed by AC10 Tech
on
Friday, March 02, 2018
Rating:
Reviewed by AC10 Tech
on
Friday, March 02, 2018
Rating: